Type 2 diabetes is a chronic metabolic disorder that affects the way your body processes glucose, a form of sugar. It is the most common type of diabetes, accounting for approximately 90% of all diabetes cases. This disease occurs when the body becomes resistant to insulin, a hormone that helps regulate blood sugar levels, or when the pancreas does not produce enough insulin.
In this article, we will explore the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of type 2 diabetes, and how it affects individuals’ lives.
Definition of Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition that affects the body’s ability to process glucose. Glucose is a type of sugar that is a major source of energy for the body. Insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas, helps the body use glucose for energy. In type 2 diabetes, the body becomes resistant to insulin or does not produce enough insulin, leading to high blood sugar levels.
Causes of Type 2 Diabetes
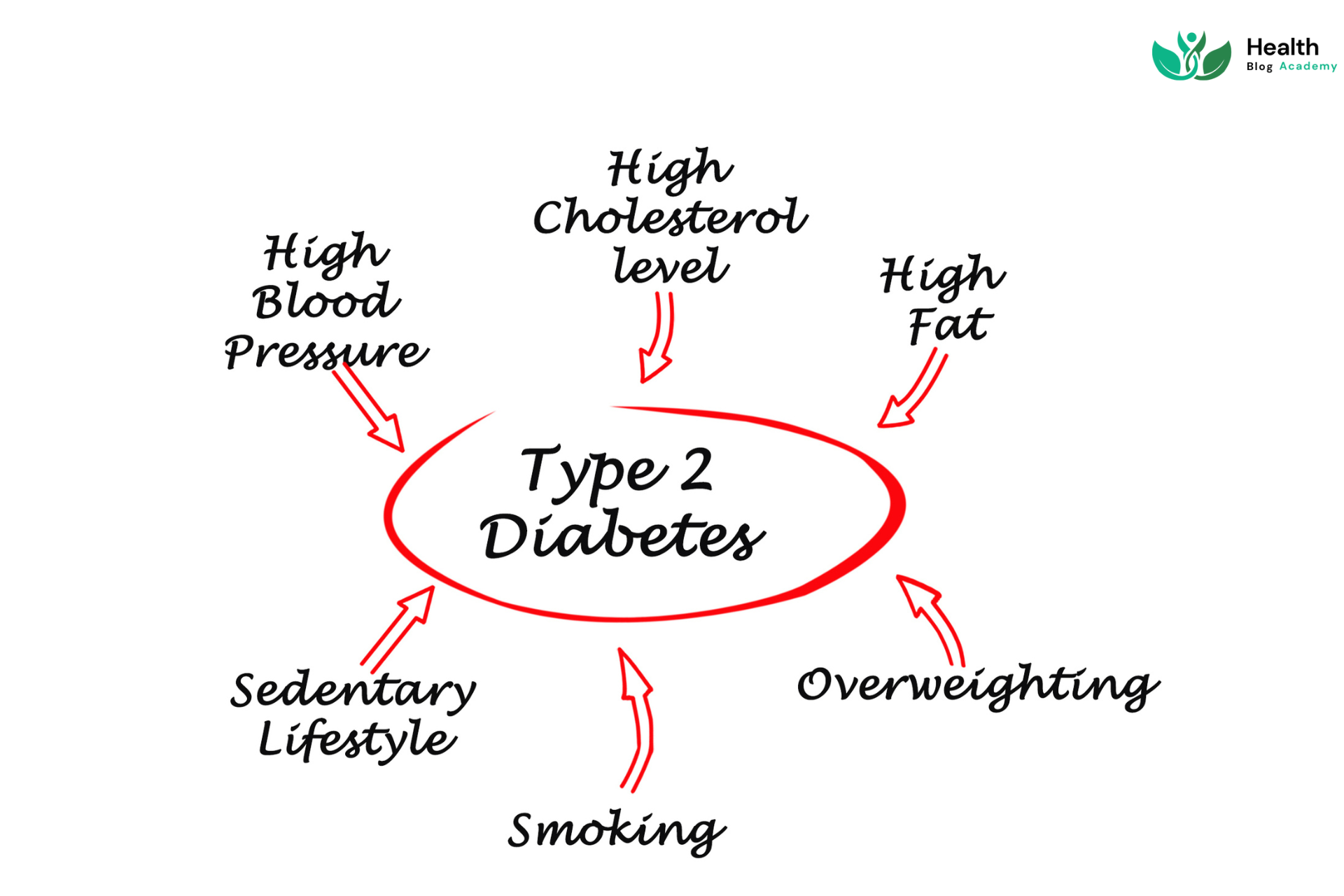
The exact cause of type 2 diabetes is not fully understood. However, several factors can increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes, including:
- Obesity or being overweight
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Family history of type 2 diabetes
- Age
- High blood pressure
- High cholesterol
- Gestational diabetes during pregnancy
- Polycystic ovary syndrome
Symptoms of Type 2 Diabetes
Some of the common symptoms of type 2 diabetes include:
- Increased thirst and hunger
- Frequent urination
- Fatigue
- Blurred vision
- Slow healing of wounds or sores
- Numbness or tingling in the feet or hands
- Recurring infections, such as yeast infections
Diagnosis of Type 2 Diabetes
Diagnosing type 2 diabetes involves several tests, including:
- A1C test: This test measures the average blood sugar level over the past 2-3 months.
- Fasting blood sugar test: This test measures the blood sugar level after an overnight fast.
- Oral glucose tolerance test: This test measures the blood sugar level after drinking a sugary drink.
Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes

The treatment of type 2 diabetes typically involves lifestyle changes, such as diet and exercise, and medications, such as insulin or oral medications that help lower blood sugar levels. The goal of treatment is to keep blood sugar levels within the normal range and prevent complications.
Prevention of Type 2 Diabetes
Preventing type 2 diabetes involves maintaining a healthy lifestyle, such as eating a balanced diet, exercising regularly, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption.
Risk Factors for Type 2 Diabetes
Several risk factors can increase the likelihood of developing type 2 diabetes, including:
- Obesity or being overweight
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Family history of type 2 diabetes
- Age: Type 2 diabetes is more common in people over the age of 45.
- Ethnicity: People of African American, Hispanic, Native American, or Asian descent are at higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
- Gestational diabetes: Women who have had gestational diabetes during pregnancy are at increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
- Polycystic ovary syndrome: Women with this condition are at higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
Complications of Type 2 Diabetes
If left untreated, type 2 diabetes can lead to several complications, including:
- Cardiovascular disease
- Nerve damage
- Kidney damage
- Eye damage or vision loss
- Foot damage or amputation
- Hearing impairment
- Alzheimer’s disease or dementia
Impact of Type 2 Diabetes on Daily Life
Type 2 diabetes can significantly impact an individual’s daily life. It requires constant monitoring of blood sugar levels, adherence to a strict diet and exercise regimen, and regular medical appointments. It can also cause fatigue, mood swings, and interfere with work or social activities.
Emotional Impact of Type 2 Diabetes
The emotional impact of type 2 diabetes should not be overlooked. It can cause feelings of anxiety, depression, and frustration, especially if it affects an individual’s quality of life. It can also impact personal relationships and social activities.
Coping with Type 2 Diabetes
Coping with type 2 diabetes involves developing a support system, staying educated about the disease, and developing healthy coping mechanisms to manage stress and anxiety. It is also important to have regular check-ups with a healthcare provider and adhere to a strict treatment plan.
Support for Type 2 Diabetes Patients
Several resources are available to support individuals with type 2 diabetes, including support groups, educational classes, and online resources. It is essential to seek support and connect with others who are going through similar experiences.
Diet and Exercise for Type 2 Diabetes

Maintaining a healthy diet and engaging in regular exercise are essential for managing type 2 diabetes. A diet that is high in fiber and low in saturated fats, sugar, and salt can help regulate blood sugar levels. Exercise can help improve insulin sensitivity and lower blood sugar levels.
Alternative Therapies for Type 2 Diabetes
Several alternative therapies, such as acupuncture and yoga, have been shown to help manage type 2 diabetes. However, it is important to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new therapy or supplement.
Conclusion
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic metabolic disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. It is a complex disease that requires a multifaceted approach to management, including lifestyle changes, medication, and regular medical appointments. It is essential to seek support and stay educated about the disease to prevent complications and improve overall quality of life.
FAQs
Q: Can type 2 diabetes be prevented?
A: A nutritious diet, frequent exercise, and keeping a healthy weight are just a few lifestyle adjustments that may help prevent or postpone type 2 diabetes. In order to track blood sugar levels and find any possible risk factors, it’s crucial to see a doctor on a regular basis.
Q: Is type 2 diabetes curable?
A: Type 2 diabetes cannot be cured, but it may be controlled with medication, lifestyle modifications, and frequent doctor visits. People with type 2 diabetes can improve their overall quality of life and delay or avoid complications by controlling their blood sugar levels.
Q: How often should I check the levels of my blood sugar?
A: Depending on the person’s treatment strategy and the advice of their medical professional, blood sugar level tests are recommended at different intervals. But the majority of people with type 2 diabetes should check their blood sugar levels frequently throughout the day, particularly before and after meals.
Q: Do you know of any all-natural treatments for type 2 diabetes?
A: Number of herbal treatments, including cinnamon and chromium supplements, has been shown to assist those with type 2 diabetes in controlling their blood sugar levels. A healthcare professional should be consulted before beginning any new treatment or supplement, however.
Q: What are some type 2 diabetes long-term complications?
A: Cardiovascular disease, nerve damage, kidney damage, eye damage or vision loss, foot damage or amputation, hearing impairment, Alzheimer’s disease, or dementia are some of the long-term effects of type 2 diabetes. Blood sugar levels may be adequately managed and a careful treatment regimen followed to avoid or postpone these consequences.

